On September 15, 2020, the research paper of Professor Zhang Qunlin’s team from the School of Pharmacy of our university entitled A New Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Specific Monitoring of hROS under Physiological Conditions Using Boric Acid-Protected L-DOPA Gold Nanoclusters was published online in Analytical Chemistry, the top journal in analytical chemistry field (IF: 6.785), and was included in Nature Index. Fang Hufeng, postgraduate of the School of Pharmacy, is the first author. Professor Zhang Qunlin and Doctor Yu Huan are joint corresponding authors.
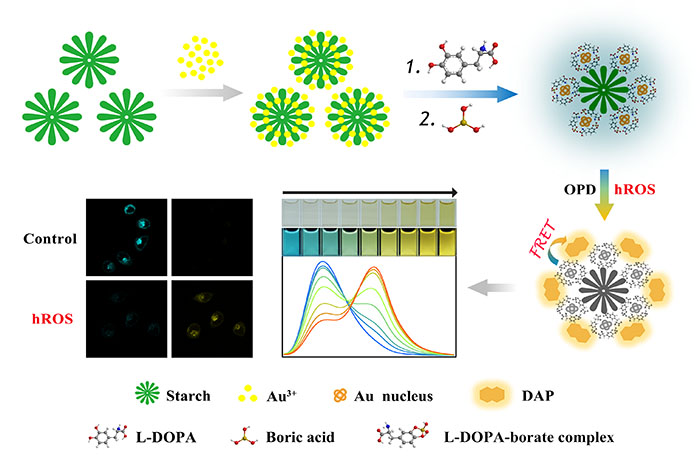
The study used starch as the template, levodopa as the reducing agent and protective agent, and boric acid as the protective group of catechol in levodopa. A small molecular ligand fluorescent nano-gold cluster with good dispersion and bio compatibility and stablility under physiological conditions was successfully synthesized for the first time. By introducing o-phenylenediamine as a fluorescence signal response reagent, a novel nanogold cluster/o-phenylenediamine ratio fluorescent probe was successfully constructed to specifically monitor the changes of intracellular hyperactive oxygen levels.
Professor Zhang Qunlin’s team has long been committed to the research and development of nano-biosensors and their diagnostic kits, which is another important research achievement after the team developed a series of nano-biosensors such as sulfhydryl amino acids, bilirubin, uric acid and alkaline phosphatase.
